Tech
What are super apps, digitalized world
Have you ever thought that instead of installing separate apps for each task in your mobile phone, there is a single portal that fulfills all your needs?
Whether you want to call a friend, send money to a loved one online, order a pizza, pay an electricity bill, book a ride, pay a child’s school fees or buy a movie ticket. You will need five to seven types of apps.
But what if all these facilities are available in a single app? This is called super app which is getting quite popular nowadays.
About 4,000 apps are registered on the Google Play Store every day, the total number of which has reached 3,480,000 by July 2022. About 2.2 million apps are registered on the Apple Store as well.
But only a few are super apps. A super app is a collection of multiple services that may not be similar to each other but are working together in a single app.
In the context of Pakistan, if Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram, Google Maps, Daraz and Easy Paisa are combined in one app, it will become a super app.
Some of the super apps:
China’s WeChat and Alipay, Singapore’s Grab, Indonesia’s GoTo, Vietnam’s Zalo and South Korea’s Kakao are super apps.
Most of them started as ride services or messaging apps and later expanded into financial services, food delivery, digital payments, gaming, travel booking, utility bill payments, airline ticketing, mobile phone top-ups, music streaming and social networking.
In today’s digital world, it is only natural for millions of users to connect with these apps. Especially in Asia, which has half of the world’s population, the reason for the success of these apps is the vast network of users.
Singapore’s Grab provides delivery, financial services and ride booking services to around 190 million customers in 428 cities across eight countries, including Thailand and Vietnam.
GoTo (GoTo) has become Indonesia’s largest tech company and a share of two percent of the GDP of one trillion dollars.
Super apps impact on economy:

87% of the South Korean population is using Kakao. However, most super apps have been successful in Asia. Europe and the US, despite being ahead of the curve in technology, will see fewer super apps. There are several reasons for this.
The first reason is how quickly people in a region accept new technology. Smart technology is quickly gaining acceptance in countries where the majority of the population consists of young people. Asia’s majority population is also young and this is the first reason why most super apps are successful in Asia.
According to a report, in terms of the number of smartphone users, China and India are leading the world, while Japan and Indonesia are also among the first ten countries.
Another reason is easy access to internet and technology. Over the past two decades, Chinese companies have made high-quality, low-cost smartphones affordable for the common man. In addition, 73 percent of Chinese have access to the Internet.
These are the two driving forces behind Alipay and WeChat becoming super apps. You can also pay via Alipay or WeChat in a Chinese village. Any app usually starts with a half-service. For example, messaging, ride sharing or delivery service. After initial success, more services are added.
A successful super app in one country is not necessarily successful in another country. Success depends on how well app developers take into account local needs and issues.

For example, Indonesia’s Gojek started as a bike ride and call center. At that time most people did not have mobile phones so the company provided easy loans to its bikers to buy mobile phones.
If you start a startup related to travel facilities, it is important that you have a thorough knowledge of the traffic situation and transport culture of your target area. In Lahore or Karachi, you cannot bring a model from China, Singapore or South Korea.
Super apps are gaining popularity not only in Asia but also in Latin American and African countries. Although there is a kind of digital gap due to economic backwardness, it is also being filled rapidly as the use of internet and smart phones is also increasing among the young generation of these countries. Chinese companies are also introducing cheap smartphones in these markets.
Why there are no super apps in europe:

There are many reasons why there are no super apps in Europe and America. Since China has created its own platforms to replace Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter and Google, the competition has not been there. Chinese companies have a large population of their own country as consumers and no competition.
But the competition between companies in America and Europe is fierce. For example, Apple’s iMessage competes with Facebook’s WhatsApp and Messenger. This competition does not allow any one company to monopolize the market in such a way that it creates a super app.
Euorope’s privacy laws are very strict:
Another reason is that data privacy laws in China are not as strict as in Europe and America. Big Chinese companies have millions of users’ data that they use for their various services, but that doesn’t mean that Chinese users don’t care about their privacy.
In contrast, Europe is very sensitive about data privacy and its laws are quite strict.
Most of the super apps depend on the data of users. They may also use user data stored for one service for another service. Which is easy in a country like China, but very difficult in Europe and America.
Super apps in Pakistan:

Officially, there is no super app in Pakistan because for a while telecom companies did not go beyond call and message service and with the presence of apps like WhatsApp and Messenger, the role of telecom companies was reduced to that of an internet provider. .
Jazz once tried to launch a super app called Veon, modeled after China’s WeChat, but it failed. Because Pakistan is not China where Google’s alternative to Baidu, Amazon’s alternative to Alibaba and Facebook and WhatsApp’s alternative to WeChat exist.
Despite this, telecom companies are offering facilities like digital payments, banking, shopping and mobile top-up through their apps. Jazz Cash, Easy Paisa and U Bank are examples of this.
Easypaisa and Jazz cash, may be a super app:
Now the specific network issue is also eliminated. Irrespective of your network, you can open an Easy Paisa account. EasyPaisa and JazzCash are providing almost all facilities except message and call. Maybe one of them will become a super app in the near future.

Tech
WhatsApp’s New Audio Call Bar Feature Simplifies Calling Experience

Digital platforms like WhatsApp work hard to improve user experience. Meta, WhatsApp’s parent company, has introduced a new feature to enhance calling. Let’s explore this addition and how it helps users.
New Whatsapp Feature:
WhatsApp’s latest feature is the Audio Call Bar feature. It aims to make calls easier for users. It’s first available to select users and will come to iOS soon.
How It Works:
When users make a call, they’ll see a new call bar. This design lets users do other things while on a call. Users can mute or end calls from the interface. When you start a call, you’ll see a new call bar at the top of the app. It stays there even if you switch to another app, making it easier to do other things while you’re on a call. You can also mute or end the call right from this bar, which saves you time and makes things simpler.
Meta’s Improvement:
Meta is committed to making WhatsApp better. They want to make it a top communication platform. It shows their aim to connect people through easy communication.
Seamless Communication:
WhatsApp’s aim is to make communicating easy. The new call bar is part of this. It keeps up their promise to help users communicate easily.
Other WhatsApp Latest Features:
Along with the call bar, there are other new whatsapp features. Apple users have passkeys for secure logins. WhatsApp’s AI assistant also does more now, like generating info and images. All these updates make using WhatsApp better.
Tech
A New Era in Space Exploration: Pakistan’s First Lunar Mission Takes Flight
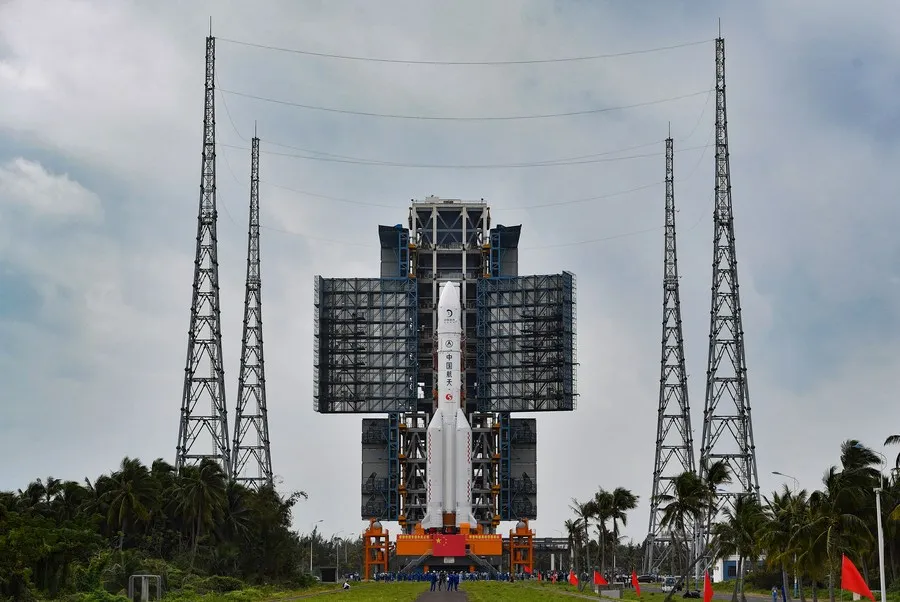

In a historic move that marks Pakistan’s debut in lunar exploration, the country’s first satellite mission named ICube Qamar was successfully launched aboard China’s Chang’e 6 mission from Hainan, China. This monumental event not only underscores the burgeoning space alliance between Pakistan and China but also signifies a pivotal moment in global lunar research efforts.
The Chang’e 6 mission, renowned for its ambitious goal to retrieve samples from the far side of the moon, took to the skies on a Long March-5 rocket from the Wenchang Space Launch Site. This mission is poised to carve a new chapter in lunar exploration by focusing on areas of the moon that have remained largely unexplored by previous missions.
Exploring the Moon’s Mysterious Far Side
China’s venture to explore the enigmatic far side of the moon showcases the nation’s advancing capabilities in space technology. The Chang’e 6 mission is designed to spend two days on the lunar surface, with plans to gather around 2 kilograms (4.4 lb) of lunar samples. These samples are anticipated to shed light on the moon’s composition and uncover secrets about its enigmatic past.
What sets this mission apart is its emphasis on collaboration. The integration of Pakistan’s ICube Qamar satellite into the mission exemplifies a global collaborative effort in the quest for lunar exploration. ICube Qamar, representing Pakistan’s inaugural venture into moon exploration, is poised to play an instrumental role in gathering data from the lunar surface, enhancing our collective understanding of the moon.
A Milestone of Collaboration
The mission’s successful launch has been greeted with widespread acclaim and enthusiasm, especially within Pakistan, where the Prime Minister has celebrated this achievement as a landmark moment for the country’s aspirations in space exploration. This event underscores the profound partnership between Pakistan and China in pushing the frontiers of space technology and exploration.
The Chang’e 6 mission, featuring payloads from various countries, serves as a testament to the spirit of international cooperation that fuels our exploration of the cosmos. Through shared resources, knowledge, and visions, nations are unlocking extraordinary possibilities in space exploration, paving the way to unravel the mysteries of our universe collectively.
Looking Ahead
The success of the Chang’e 6 mission, with Pakistan’s ICube Qamar onboard, heralds a new era of international cooperation in space exploration. It demonstrates the immense potential of collaborative missions in advancing human knowledge and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
As we await the return of the Chang’e 6 probe with samples from the moon’s far side, we stand on the brink of new discoveries that could redefine our understanding of the moon and beyond. This mission is not just a triumph for Pakistan and China but a victory for the international community’s collective endeavor to explore the unknown frontiers of space
Tech
Musk’s X Debuts its Own Version of YouTube for Smart TVs

Overview:
Musk’s brainchild, X, is ready to roll out its own television application compatible with Amazon and Samsung smart TVs. With eyes set on rivalling YouTube, the new app, set for launch next week, promises to intrigue users with longer videos on sizeable screens. Musk envisages luring digital influencers and advertisers to X, by providing a platform mirroring YouTube’s TV app. As it grows its footprint in the streaming video sector, X is also primed to battle with platforms like Twitch, Signal, and Reddit. This attempt underlines X’s ambitious transition from a text-based messaging platform to a video-focused arena.
In-depth Insights:
- Musk’s venture, X, is about to usher in its own TV app for Amazon and Samsung smart TVs, to pose a challenge to YouTube.
- The upcoming app, scheduled for release next week, is aimed at captivating users with prolonged videos on expanded screens.
- By imitating the model of YouTube’s TV app, X is geared to captivate the attention of digital influencers and advertisers.
- With a goal to vie with platforms such as Twitch, Signal, and Reddit, Musk envisions a new realm for X.
- Marking its transition to video-based content, X had earlier declared its move to imitate TikTok’s infinite scroll feature.
- Formerly known as Twitter, X has a history of launching multiple TV apps.
- As X aims to dominate the video streaming world, it focuses on celebrities, digital influencers, and video game streaming.
- X has successfully initiated contracts with media personalities Don Lemon and Tucker Carlson for exclusive shows.
- X has been motivating content creators to shift their video content to its platform, guaranteeing increased ad revenue.
- Mr. Beast, a renowned YouTuber, contributed to X’s testing phase by uploading a full-length video and revealing his earnings.
- With a reported decline in user engagement by 30% and loss of significant advertisers, X is grappling to retain its user base and advertising partners.
- Musk’s ownership of X has witnessed a substantial devaluation in its overall assessment.
Source: Fortune.com
-

 Tech3 months ago
Tech3 months agoWhatsApp’s New Audio Call Bar Feature Simplifies Calling Experience
-

 Phones3 months ago
Phones3 months agoInfinix Zero 30 (4G vs. 5G): Specifications, Features, and Prices in Pakistan
-

 Phones3 months ago
Phones3 months agoEverything You Need to Know About Jazz Digit 4G Mobile Phones in Pakistan
-

 Mobile Packages3 months ago
Mobile Packages3 months agoHow to Check Your Telenor, Zong, Ufone, Jazz SIM Number
-

 Tech3 months ago
Tech3 months agoGuide to Blocking and Unblocking Users on Snapchat
-

 iPhone3 months ago
iPhone3 months agoExploring JV iPhones: Prices, Risks, and Rewards in Pakistan
-

 Phones3 months ago
Phones3 months agoZTE Axon 60 Series: Affordable 4G Phones with Unisoc Chipsets
-

 Tech3 months ago
Tech3 months agoA New Era in Space Exploration: Pakistan’s First Lunar Mission Takes Flight



